Understanding Cloud-Based Data Storage
Before we dive into performance metrics, let's understand what cloud-based data storage is, why performance matters, and which components directly affect its speed and reliability.
What is Cloud-Based Data Storage?
Cloud-based data storage is a digital solution that allows users and organizations to store, manage, and access their files, databases, and backups on remote servers hosted over the internet—rather than maintaining physical hardware on-site. The data is stored across secure, high-performance data centers managed by providers such as Amazon Web Services (AWS), Google Cloud, and Microsoft Azure.
This model provides on-demand scalability, enhanced accessibility, and built-in disaster recovery. With cloud-based data storage, teams can collaborate globally, access data from any device, and benefit from enterprise-grade security without investing in complex infrastructure while accelerating secure and scalable cloud-based app development. It’s especially beneficial for enterprises seeking secure cloud-based data storage services with ISO 27001 certification, or those requiring multi-region cloud-based data storage platforms to support global collaboration and compliance.
There are 3 main types of Cloud-Based Data Storage:
- Object Storage: Ideal for unstructured data like images, videos, documents, and backups. (Example: Amazon S3)
- Block Storage: Best for structured workloads such as databases and virtual machines requiring high-speed read/write operations. (Example: AWS EBS)
- File Storage: Designed for shared file systems that allow multiple users or applications to access and modify files simultaneously. (Example: Azure Files)
Why Cloud-Based Data Storage Performance Matters
While cloud-based data storage offers scalability and flexibility, performance still plays a crucial role in how effectively data can be accessed, processed, and delivered — especially for enterprises relying on high-performance cloud-based data storage solutions for analytics workloads or cost-efficient cloud-based data storage architecture design and consulting. Here are 3 key reasons:
- User Experience: Faster data retrieval ensures seamless collaboration and productivity.
- Application Efficiency: Applications relying on quick data access perform more reliably when latency is minimized.
- Operational Costs: Efficient storage reduces data transfer time and optimizes cloud resource usage.
A strong cloud-based data storage performance foundation keeps data accessible, applications stable, and business operations smooth at scale.
Key Components Influencing Cloud-Based Data Storage Performance
Several factors determine how well your cloud-based data storage system performs, Here are the major ones:
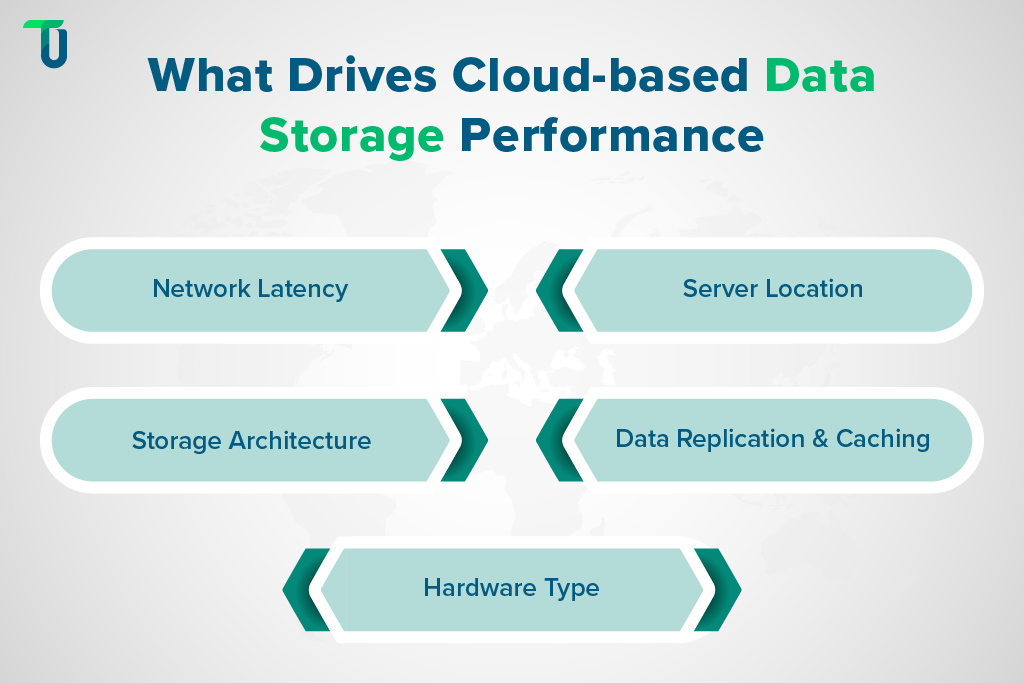
- Network Latency: The time it takes for data to travel between user and server.
- Server Location: The closer the data center to your users, the faster the response time.
- Storage Architecture: Object, block, and file storage perform differently depending on the workload.
- Data Replication and Caching: Replication enhances reliability, while caching speeds up frequently accessed data.
- Hardware Type: SSD-backed storage usually performs faster than HDD-based systems.
Understanding these components helps businesses design the right cloud-based data storage architecture—one that aligns with their performance, reliability, and scalability goals and follows best practices in High-Performance Cloud Architecture Design.
Choose the Right Cloud Storage Provider with TenUp
Let us help you evaluate providers and design a cloud-based storage solution that fits your performance and budget needs.
Core Metrics for Evaluating Cloud Storage Speed
Measuring how effectively your cloud-based data storage performs starts with understanding the key metrics that define speed, responsiveness, and reliability. These metrics provide insight into how efficiently your data moves, how well applications interact with storage systems, and where optimization is needed.
The four fundamental performance indicators for cloud-based data storage are latency, throughput, IOPS, and read/write speed. Each one helps assess how your cloud environment handles workloads, user requests, and data transfer operations.
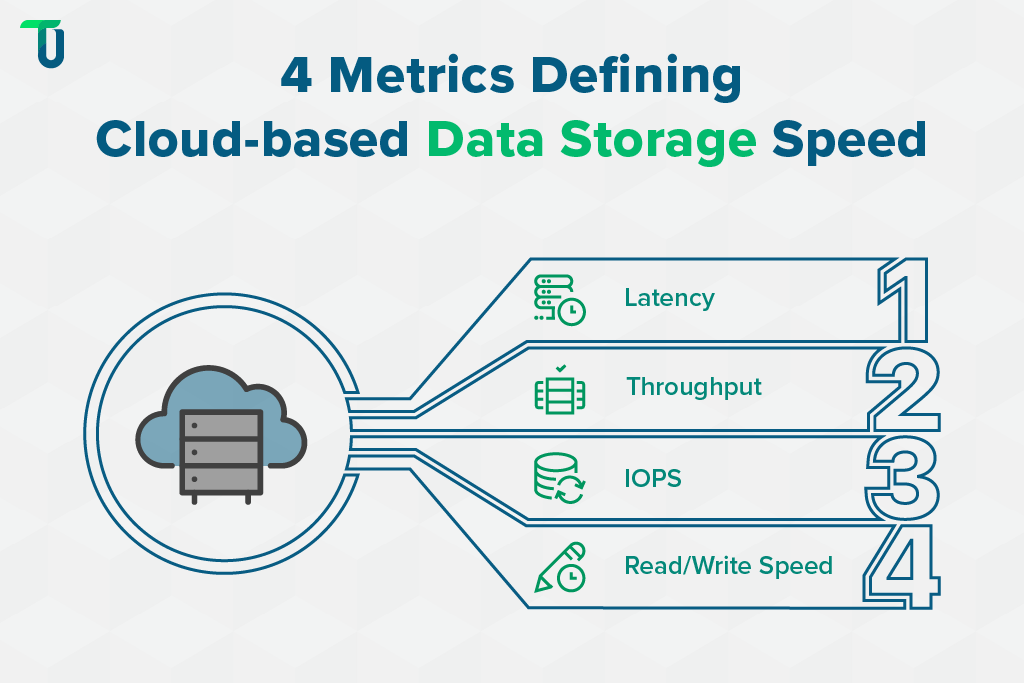
1. Latency
Latency measures the time it takes for data to travel from the source to the destination within a cloud-based data storage environment. It directly affects how responsive an application feels. Lower latency means faster access and smoother operations.
- Low latency is critical for real-time systems like video conferencing, trading platforms, or online transactions.
- High latency can cause noticeable delays, slow retrievals, and reduced application performance.
Factors such as network distance, routing paths, and the provider’s infrastructure design all influence latency.
Keeping latency low ensures your cloud-based data storage system delivers consistent performance across regions and workloads.
2. Throughput (or Bandwidth)
Throughput, often linked to bandwidth, shows how much data can be transferred per second within a cloud-based data storage system. It represents the system’s maximum data-handling capacity and determines how efficiently uploads, backups, and migrations occur.
- Higher throughput supports faster uploads, backups, and data migration.
- Lower throughput restricts large file transfers and slows down multi-user access.
Throughput depends on factors like network bandwidth, file size, and concurrent data requests.
Optimizing throughput helps maintain steady performance as your cloud-based data storage scales with larger datasets and global users.
3. IOPS (Input/Output Operations per Second)
IOPS indicates how many read and write operations your cloud-based data storage can perform each second. It is vital for databases and transaction-heavy applications.
- Higher IOPS means better performance under heavy workloads.
- Lower IOPS leads to lag during simultaneous operations.
Storage medium type (SSD, HDD, or object storage) directly affects achievable IOPS levels.
Monitoring IOPS helps ensure your cloud-based data storage architecture can handle demanding, data-intensive workloads without performance drops.
4. Read/Write Speed
Read/write speed defines how quickly data can be retrieved (read) or saved (write) in your cloud-based data storage system. It influences everything from real-time analytics to backups and content creation.
- Fast read speed boosts analytics and reporting performance.
- Fast write speed accelerates data ingestion, backups, and content creation.
These speeds vary based on file size & type, caching mechanisms, and network conditions.
Must-Read for Data Professionals
Evaluating Reliability and Availability in Cloud-Based Data Storage
According to Gartner, over 70% of enterprise workloads now rely on cloud-based data storage for primary and backup operations, making reliability and availability top priorities in infrastructure planning.
Reliability and availability are two of the most critical pillars of cloud-based data storage. They determine how consistently your data stays accessible, accurate, and protected against loss or downtime. Businesses rely on these metrics to choose cloud-based data storage systems that minimize operational disruptions and ensure long-term data integrity.
To assess reliability, organizations should evaluate four key metrics — uptime, data durability, fault tolerance, and consistency. Together, they define how dependable and resilient a cloud-based data storage environment truly is.
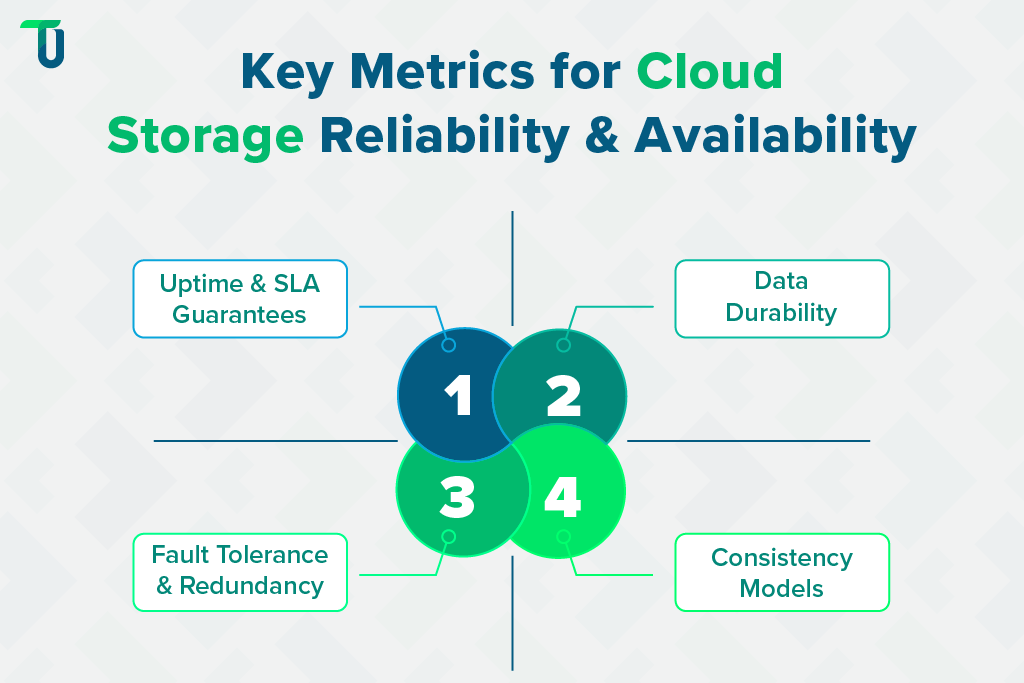
A. Uptime and SLA Guarantees
Uptime measures how often a cloud-based data storage service remains available and operational. Leading providers such as AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud define their Service Level Agreements (SLAs) in terms of guaranteed uptime, typically expressed as a percentage.
Why it Matters: High uptime ensures applications run continuously and prevents revenue loss or productivity disruptions caused by system downtime.
How to Calculate:
Uptime (%) = (Total Time – Downtime) / Total Time * 100
For example, 99.9% uptime allows roughly 8.7 hours of downtime per year, while 99.99% reduces it to less than an hour.
- Best Practice: Continuously monitor real-world uptime using external tools to validate SLA compliance.
Maintaining high uptime guarantees stable and predictable cloud-based data storage performance across workloads.
B. Data Durability
Data durability reflects the probability that information stored in your cloud-based data storage system remains intact, uncorrupted, and retrievable over time. Cloud systems achieve high durability through replication across multiple devices and geographic regions.
Why it Matters: Durable storage protects critical business data from permanent loss due to hardware failures or disasters.
How to Calculate:
Durability is typically expressed in “nines.” For example, 99.999999999% (“11 nines”) means the probability of data loss in a given year is extremely low.
- Best Practice: Review your provider’s replication and backup policies to ensure compliance with enterprise continuity standards and consider an ISO 27001-compliant cloud migration strategy when designing failover and replication plans.
High durability ensures your cloud-based data storage architecture maintains business continuity and data safety, even under failure conditions.
C. Fault Tolerance and Redundancy
Fault tolerance represents the ability of a cloud-based data storage solution to keep functioning when components fail. Redundancy involves duplicating data across multiple storage nodes or regions to prevent loss.
Why it Matters: Redundant, fault-tolerant systems maintain data availability during hardware failures, network outages, or accidental deletions, minimizing operational risk.
How to Calculate: Evaluate the number of replicas, geographic distribution, and failover mechanisms. Multi-zone and multi-region replication strategies offer higher fault tolerance.
- Best Practice: Periodically simulate failover events to verify how quickly your cloud-based data storage system recovers after disruption.
Redundancy and fault tolerance reduce the risk of service disruption and help maintain uninterrupted access to data.
D. Consistency Models
Consistency determines how quickly updates to data appear across all storage copies. Cloud storage may use strong consistency or eventual consistency models depending on architecture and workload requirements.
Why it Matters: Test read-after-write scenarios across regions. Strong consistency returns updated data immediately, while eventual consistency may show older data for a short period. Understanding workload needs to choose the right model.
- Strong Consistency: Guarantees every read reflects the latest write, essential for transactional systems (e.g., banking, e-commerce).
- Eventual Consistency: Offers better scalability and performance for large distributed environments but may momentarily show older data.
How to Calculate: Test read-after-write scenarios across regions. Strong consistency returns updated data immediately, while eventual consistency may show older data for a short period. Understanding workload needs to choose the right model.
By evaluating these metrics- uptime, durability, redundancy, and consistency, you can get a clear view of cloud-based data storage reliability.
Related Articles:
Tools and Techniques for Measuring Cloud-Based Data Storage Performance
Monitoring and optimizing cloud-based data storage performance requires the right set of tools and techniques. These tools help organizations track latency, throughput, IOPS, and reliability metrics in real time—ensuring that their cloud infrastructure runs efficiently and meets business expectations.
To effectively evaluate your cloud-based data storage system, you can rely on three main categories of performance measurement tools: provider-built monitoring tools, third-party benchmarking platforms, and custom testing methods.
A. Cloud Provider Tools
Most major clouds like AWS, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud providers offer built-in monitoring tools that allow teams to track cloud-based data storage metrics directly within their environments. These tools allow users to track latency, throughput, and error rates without external software.
- AWS CloudWatch and S3 Metrics: Track request counts, latency, error rates, and throughput for Amazon S3 buckets and EBS volumes.
- Azure Monitor: Tracks read/write latency, transaction counts, and overall availability for Azure Blob Storage.
- Google Cloud Monitoring: Displays storage latency, request rates, and error percentages for GCS (Google Cloud Storage) buckets and persistent disks.
These tools simplify cloud-based data storage monitoring and optimize cloud performance, providing historical insights and trend analysis without requiring external integrations.
B. Third-Party Benchmarking Tools
External benchmarking tools provide independent performance comparisons across different cloud-based data storage providers. These tools simulate workloads and produce standardized performance metrics, offering a transparent view beyond provider-reported data.
- PerfKit Benchmarker: Developed by Google, this open-source tool measures latency, throughput, and IOPS for multiple cloud environments.
- CloudHarmony: Offers performance scores and benchmarks for major cloud storage providers.
- Fio (Flexible I/O Tester): Runs advanced read/write tests with various block sizes and patterns to assess throughput and IOPS.
Using third-party benchmarks helps validate provider claims and gives organizations an objective way to compare cloud-based data storage performance before choosing a long-term solution.
C. DIY Testing Methods
For more hands-on analysis, businesses can conduct their own tests to evaluate how cloud-based data storage systems perform under real-world workloads. These do-it-yourself (DIY) approaches are ideal for customized environments or hybrid architectures.
- Upload/Download Tests: Measure time to transfer large files from multiple locations to estimate latency and throughput.
- Latency Checks: Ping storage endpoints from different regions to evaluate response times.
- Monitoring Tools: Tools like UptimeRobot and Pingdom track availability and detect performance fluctuations.
DIY testing provides granular insights into the behavior of your cloud-based data storage architecture, enabling teams to identify bottlenecks, improve configurations, and enhance reliability based on actual usage patterns.
TenUp’s Take: Cloud storage is more than just space. Understanding latency, throughput, IOPS, and redundancy helps businesses make informed choices, keeping data accessible, applications responsive, and operations efficient across all environments.
Performance Optimization Tips
To achieve maximum efficiency from your cloud-based data storage, it’s essential to optimize configuration settings, data placement, and access patterns. Well-tuned systems deliver faster data retrieval, better cost management, and greater reliability, all critical for businesses managing large-scale, distributed workloads.
Below are seven practical tips to help you enhance the speed, reliability, and scalability of your cloud-based data storage system:
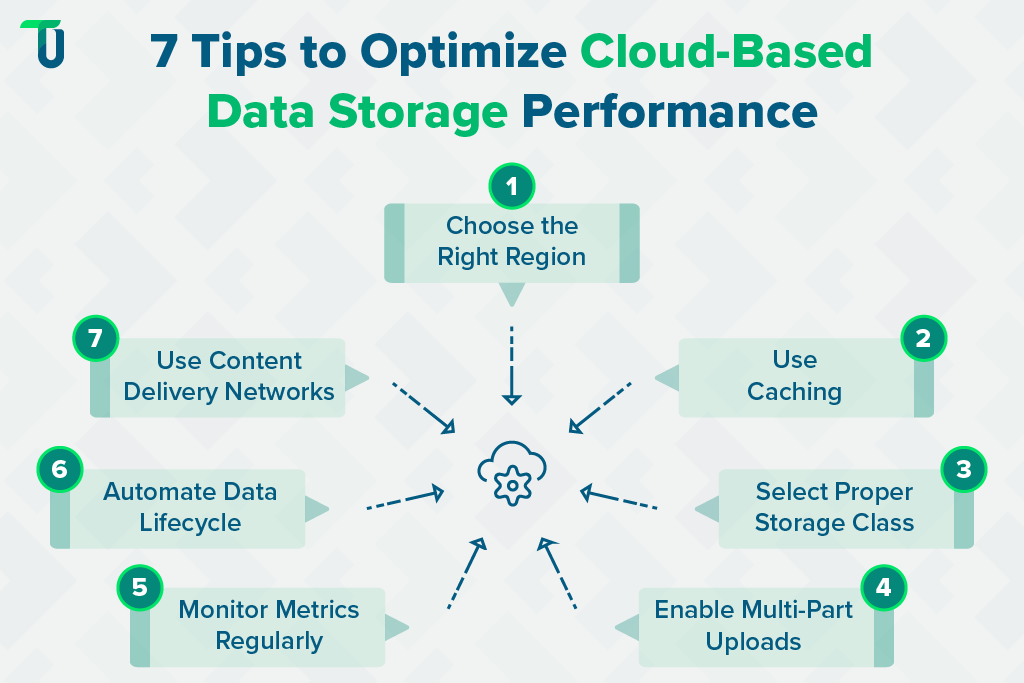
Tip #1: Choose the Right Region: Select data centers located closest to your users or core operations. Placing data in a nearby region minimizes latency and improves access speed, ensuring your cloud-based data storage delivers consistent performance for end-users across geographies.
Tip #2: Use Caching: Use caching mechanisms to store copies of frequently accessed files. This reduces repetitive fetches from the main cloud-based data storage and significantly improves read speeds for applications that rely on real-time data delivery.
Tip #3: Select Proper Storage Class: Cloud providers offer multiple storage classes tailored to different workloads. Use high-performance tiers for active applications and cost-efficient tiers for backups or archived data. Aligning workloads with the right class ensures that your Secure and scalable cloud storage architecture balances cost and performance effectively.
Tip #4: Enable Multi-Part Uploads: When handling large files, divide them into smaller chunks for parallel uploads. This technique accelerates write operations and improves upload reliability, particularly for object-based cloud data storage solutions such as Amazon S3 or Google Cloud Storage.
Tip #5: Monitor Metrics Regularly: Track latency, throughput, and IOPS using built-in dashboards or third-party tools. Continuous monitoring helps identify performance bottlenecks early, allowing you to fine-tune your cloud-based data storage system for optimal results.
Tip #6: Automate Data Lifecycle: Configure lifecycle policies to automatically move inactive or rarely accessed data to low-cost storage tiers. This practice reduces operational expenses, optimizes storage performance, and ensures efficient resource allocation in your cloud-based data storage environment.
Tip #7: Use Content Delivery Networks (CDN): For globally distributed users, integrate CDNs to deliver static assets from edge locations closer to end-users. CDNs complement cloud-based data storage by reducing latency, improving download speeds, and enhancing user experience worldwide.
Following these practical tips helps cloud-based data storage run faster, maintain reliability, and deliver consistent performance for applications and end-users.
Comparing Popular Cloud-Based Data Storage Providers
Choosing the right cloud-based data storage provider is a critical step in ensuring that your infrastructure meets your business’s performance, scalability, and compliance requirements. Each major provider offers unique strengths and trade-offs across metrics like durability, reliability, cost structure, and ecosystem integration.
Below, we compare the leading cloud-based data storage solutions from Amazon Web Services, Google Cloud, Microsoft Azure, and IBM — helping you evaluate which best fits your workloads and strategic goals. For a side-by-side analysis see AWS Azure and Google Cloud Storage Comparison.
1. Amazon Web Services (AWS S3)
AWS S3 is a widely used object storage service offering high durability and availability. It provides multiple storage classes, global replication, and seamless integration with other AWS services. It supports a variety of workloads, from backup and archiving to high-performance analytics and content distribution, making it suitable for enterprises of all sizes.
Pros of AWS S3:
- Offers 99.999999999% data durability across regions
- Multiple storage classes for cost and performance balance
- Strong ecosystem integration with analytics and compute services
Cons of AWS S3:
- Data transfer costs increase with frequent access
- Complex pricing can confuse new users
Ideal Use Case: Large-scale enterprises requiring globally distributed, high-performance cloud-based data storage with extensive ecosystem integration.
2. Google Cloud Storage (GCS)
Google Cloud Storage provides scalable object storage with automatic multi-region replication and strong integration with Google’s analytics and AI services. It supports high-throughput workloads, ensuring fast access to data. GCS is suited for applications that rely on machine learning, analytics pipelines, or content delivery across different geographic regions.
Pros of Google Cloud Storage:
- Automatic data replication across regions
- Strong integration with AI and analytics tools
- Scalable performance for large data workloads
Cons of Google Cloud Storage:
- Slightly complex tier structure may affect cost management
- Fewer regions than some competitors
Ideal Use Case: Businesses handling data-intensive workloads such as machine learning pipelines, analytics, or content delivery that demand flexible cloud-based data storage scalability.
3. Microsoft Azure Blob Storage
Azure Blob Storage is optimized for enterprise applications, offering object storage with hot, cool, and archive tiers. It provides integration with Microsoft’s ecosystem and supports hybrid cloud architectures. The storage service works well for mission-critical workloads, backups, and collaboration across global teams, with strong security and compliance features for corporate environments.
Pros of Azure Blob Storage:
- Flexible tier options for cost management
- Strong enterprise security and compliance features
- Supports hybrid cloud integration easily
Cons of Azure Blob Storage:
- Performance may vary across regions
- Pricing complexity for high-volume storage
Ideal Use Case: Enterprises needing secure, hybrid-ready cloud-based data storage systems that align with Microsoft’s ecosystem and compliance standards.
4. IBM Cloud Object Storage
IBM Cloud Object Storage focuses on durability, security, and compliance for regulated industries. It offers advanced encryption, multiple redundancy options, and policies for data retention and lifecycle management. The service is designed for enterprise workloads where data integrity, regulatory compliance, and long-term storage reliability are top priorities.
Pros of IBM Cloud Object Storage:
- Highly secure with advanced encryption
- Multiple redundancy and replication options
- Compliance support for regulated industries
Cons of IBM Cloud Object Storage:
- Limited global data center presence
- Fewer integration options than larger providers
Ideal Use Case: Organizations in regulated industries needing secure, compliant, and reliable cloud-based data storage with long-term data integrity guarantees.
Related Read:
Cloud App Development: AWS vs Azure vs Google Cloud
| AWS S3 | Google Cloud Storage | Azure Blob Storage | IBM Cloud Object Storage | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Availability | 99.99% | 99.95% | 99.95% | 99.99% |
| Durability | 11 nines | 11 nines | 11 nines | 11 nines |
| Pros | Durable, versatile, integrated | Multi-region, AI integration, scalable | Flexible tiers, secure, hybrid support | Secure, redundant, compliant |
| Cons | Expensive transfers, complex pricing | Tier complexity, fewer regions | Regional performance, pricing complexity | Limited regions, fewer integrations |
| Ideal Use Case | Large-scale global apps | Analytics and ML workloads | Hybrid enterprise solutions | Regulated industry storage |
As we can see, each cloud-based data storage provider offers distinct strengths and trade-offs. Consider these factors carefully to select the solution that best fits your specific workloads and requirements.
Scale Securely with Optimized Cloud-Based Data Storage
Evaluating cloud-based data storage performance is essential for ensuring fast, reliable, and cost-effective access to data. As most businesses now rely on cloud-based data storage solutions (with over 70% of enterprises using cloud infrastructure, according to Gartner), choosing and optimizing the right system is critical.
Make sure you consider key metrics such as latency, throughput, IOPS, read/write speed, uptime, durability, fault tolerance, and consistency, as explained in this blog. If you lack the resources or expertise to assess and optimize cloud-based data storage, consider our cloud optimization consulting for hands-on assessment and optimization.
TenUp is an ISO 27001-certified software development company and a trusted AWS partner. Our team of 70+ certified professionals, including AWS-certified architects and engineers, specializes in building secure, scalable, and cost-effective cloud-based data storage solutions tailored to your business needs.
Get in touch with our experts today to build a reliable and future-ready cloud-based data storage system for your organization.
Achieve Peak Cloud Storage Performance with TenUp
Boost your enterprise storage with our AWS-certified engineers. Optimize latency, throughput, and data reliability efficiently.
Frequently asked questions
What is cloud-based data storage and how does it work?
Cloud-based data storage lets users save and access data online instead of local hardware. It works by uploading files to secure, third-party data centers where data is replicated across multiple servers for durability and uptime. This ensures high availability, scalability, and real-time access while the provider manages security and infrastructure. However, not all providers guarantee real-time access, and security management responsibilities are shared under the shared responsibility model.
Which performance metrics matter most for cloud-based data storage?
The most important performance metrics for cloud-based data storage are latency, throughput, IOPS, and read/write speed. Together, they determine how fast data moves, how many operations a system can handle, and how responsive applications remain under load. These metrics directly impact storage reliability, scalability, and user experience.
How do I choose between object block and file storage for cloud-based data storage?
Choose object storage for scalable, unstructured data like media or backups, block storage for high-performance workloads such as databases and virtual machines, and file storage for shared, hierarchical data access across teams. Match each type to your workload’s structure, latency, and scalability needs.
What is the fastest way to reduce latency in cloud-based data storage?
To reduce latency in cloud-based data storage, store data in regions closest to users, use caching or a CDN for frequently accessed content, and enable multi-region replication or edge computing. These strategies minimize network distance, boost response speed, and ensure faster global access.
How do cloud providers differ for enterprise cloud-based data storage?
Cloud providers differ in storage performance, ecosystem integration, and compliance features. AWS offers flexible storage classes and global scalability, Google Cloud excels in analytics and high-throughput workloads, while Azure stands out for hybrid deployment and enterprise security. Each varies in pricing, regional coverage, and native management tools.
What is data durability and how is it expressed for cloud-based data storage?
Data durability measures how reliably cloud-based data storage preserves information over time. It’s expressed in “nines” (e.g., 99.999999999% or 11 nines), indicating an extremely low chance of data loss. Higher nines mean greater resilience through redundancy, replication, and automated recovery across cloud regions.
Which benchmarking tools provide objective cloud-based data storage performance tests?
The most reliable tools for testing cloud-based data storage performance are PerfKit Benchmarker and Fio. PerfKit offers cross-cloud, standardized benchmarks, while Fio simulates detailed I/O patterns to measure IOPS, latency, and throughput under real-world workloads, ensuring objective, comparable performance results.
How can automating data lifecycle policies help cloud-based data storage costs and performance?
Automating data lifecycle policies cuts cloud storage costs by shifting infrequently accessed data to lower-cost tiers and deleting outdated files. It also boosts performance by keeping active data on high-speed storage, improving responsiveness while reducing manual management overhead and ensuring consistent compliance.

